00 - Intro to subject - TDBM
00 - Intro to subject - TDBM
In this course we will study the UTP ([[Urban Transportation Planning]]) 4 stage framework:
- [[#1 - Data Collection]]
- [[#2 - Modeling]]
- [[#3 - Forecasting]]
- [[#4 - Evaluation]]
Classic 4 stage framework
The classic 4 stage framework is also called trip-based approach. This is because it relies trip as unit of analysis. This approach is described in the following paragraph but is becoming more and more limited in the ability to model people mobility as it cannot account for [[Intermodality]] (using more than one mode of transportation for one trip). Therefore, a new approach has been proposed and is gaining popularity: the [[#Activity-based modeling]].
As the name suggests, the framework is made of 4 stages:
- [[#1 - Data Collection]]
- [[#2 - Modeling]]
- [[#3 - Forecasting]]
- [[#4 - Evaluation]]
1 - Data Collection
This is the first stage of the UTP 4 stage framework.
At this stage we need:
- Socio-economic and land use data
- Define zonizzazione)
- Define transportation infrastructure (network)
All the data that is available needs to be grouped by TAZ
2 - Modeling
In the modeling stage, we apply a 4 steps modeling process (see also: modello a 4 stadi). This is actually the union of 4 models that describe different aspects of transportation:
- [[#I - Trip generation]]
- [[#II - Trip Distribution]]
- [[#III - Mode choice]]
- [[#IV - Route choice]]
In the modeling stage we also need to account for the purpose of a trip. This is usually done evaluating the 4 steps for each and every purpose.
For example, we will have Generation, Distribution, Mode choice and Route choice for school trips, for work trips, for leisure trips, and so on...
The results of this model will go into an OD matrix (see matrici origine-destinazione). To be precise, they will go into a set of OD matrixes, one for each purpose.
where:
number of trips from TAZ to TAZ tot number of trips generated by TAZ - It's the sum of the colums
tot number of trips attracted by TAZ - It's the sum of the rows
tot number of TAZs
I - Trip generation
In trip distribution, we model the total trip Production (
This is done usually through linear regression models. We will obtain (for origin
After this step, we have models for real
Trip generation is addressed in details in 03 - Trip generation modeling - TDBM.
II - Trip distribution
In this step we fill in every
In short, with this step we obtain the cumulated values (by mode and route) for
This step is addressed in details in 04 - Trip Distribution Modeling - TDBM.
III - Mode choice
In this step we model how many trips from
IV - Route choice
This is the assignment step where we start from a network and matrixes and we assign each trip to a specific route, combining road paths to Public Transportation.
3 - Forecasting
The stage 3 includes the forecasting in the future of demand, according to new land use and/or changes in the Transport System
4 - Evaluation
The stage 4 includes the evaluation of every scenario and alternatives
Activity-based modeling
This is an alternative approach from the #Classic 4 stage framework, where the base unit of analysis is shifted from the trip and the person becomes the center of the modeling. In this approach we basically consider the whole day of a person and all the activity they do
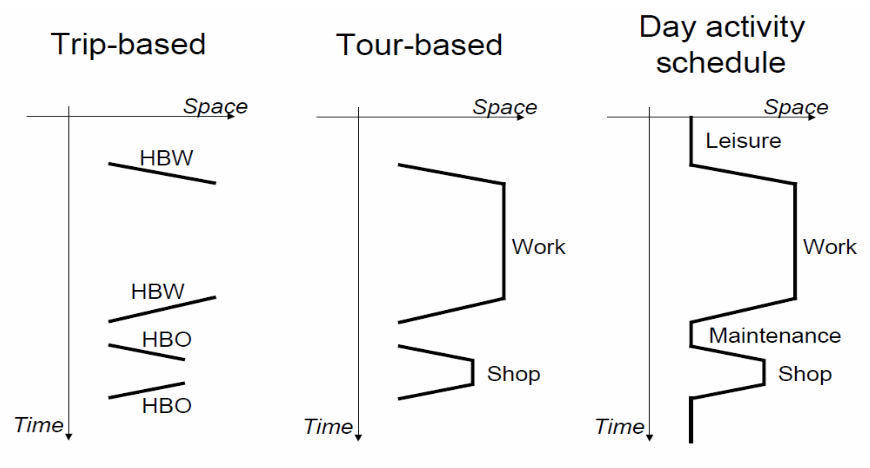
The basic approach still remains valid. We still use OD matrices and the zoning system (TAZ).