06 - Public Private Partnership - DME
06 - Public Private Partnership - DME
Public financing
Necessity: There are Important infrastructure investment needs due to:
- Structural deficiencies of economy
- Having to cover needs not covered by private sector
- Increase efficiency of public sector
There are 3 ways of public financing:
- Direct:
- The administration finances and manages the investment
- Deferred:
- The financial burden is delayed
- Indirect:
- Administration finances but does not manage the investment (EU funds)
Types of public funding
Direct public funding
In Direct public funding, the government raises funds immediatly and pays for a project directly.
For example, building a new highway funded by government bonds.
Deferred public funding
In Deferred public funding, the financial burden of the project is delayed to a future date.
For example, a company builds a hospital and the government pays for it over 20 years.
Indirect public financing
In Indirect public financing, the public, more than paying, makes incetives, through garantees, subsidies, without directly raising or spending funds.
For example, offering tax breaks to developers who invest in renewable energy projects.
Some models
Public funds to public entities
A way of [[#Indirect public financing]] an infrastructure.
A public or private agent is created for the sole purpose of managing and executing a project. The public administration funds this entity.
This can happen in 3 different ways:
- [[#Public funds to public entities from chapter VII]]
- [[#Public funds to instrumental societies]]
- [[#Contributions to public business entities or state owned companies under chapter VIII]]
Public funds to public entities from chapter VII
Capital transfers taken from the budget to whoever is managing the project.
Public funds to instrumental societies
Create a company or other public entity for the sole purpose of managing a project with NO commercial income. Public funds reimburse all expenses annually.
Contributions to public business entities or state owned companies under chapter VIII
Similar to [[#Public funds to instrumental societies]] but the company has commercial income. It needs to be profitable.
Deferred or fraction payment
There is a Construction contract such that, in exchange for a single price, the contractor finances the construction, then, when the work is done, it gets payed back.
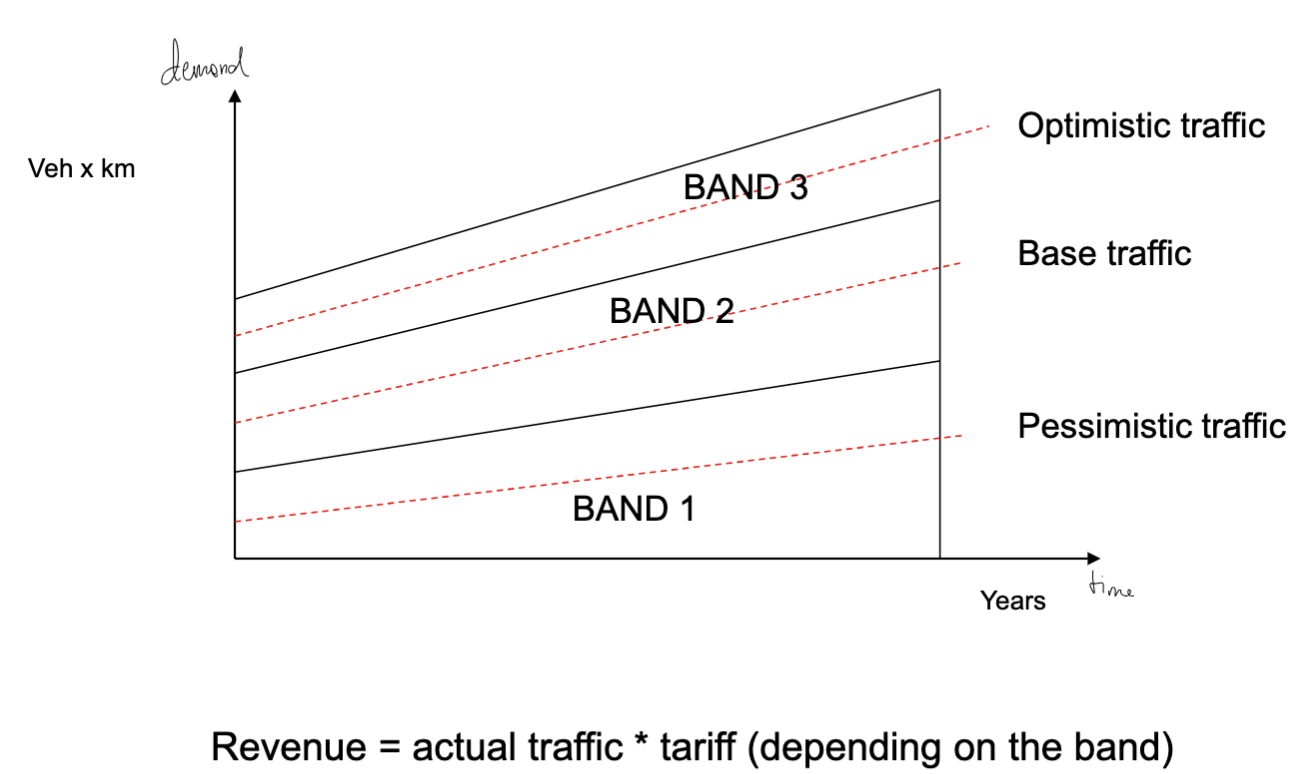
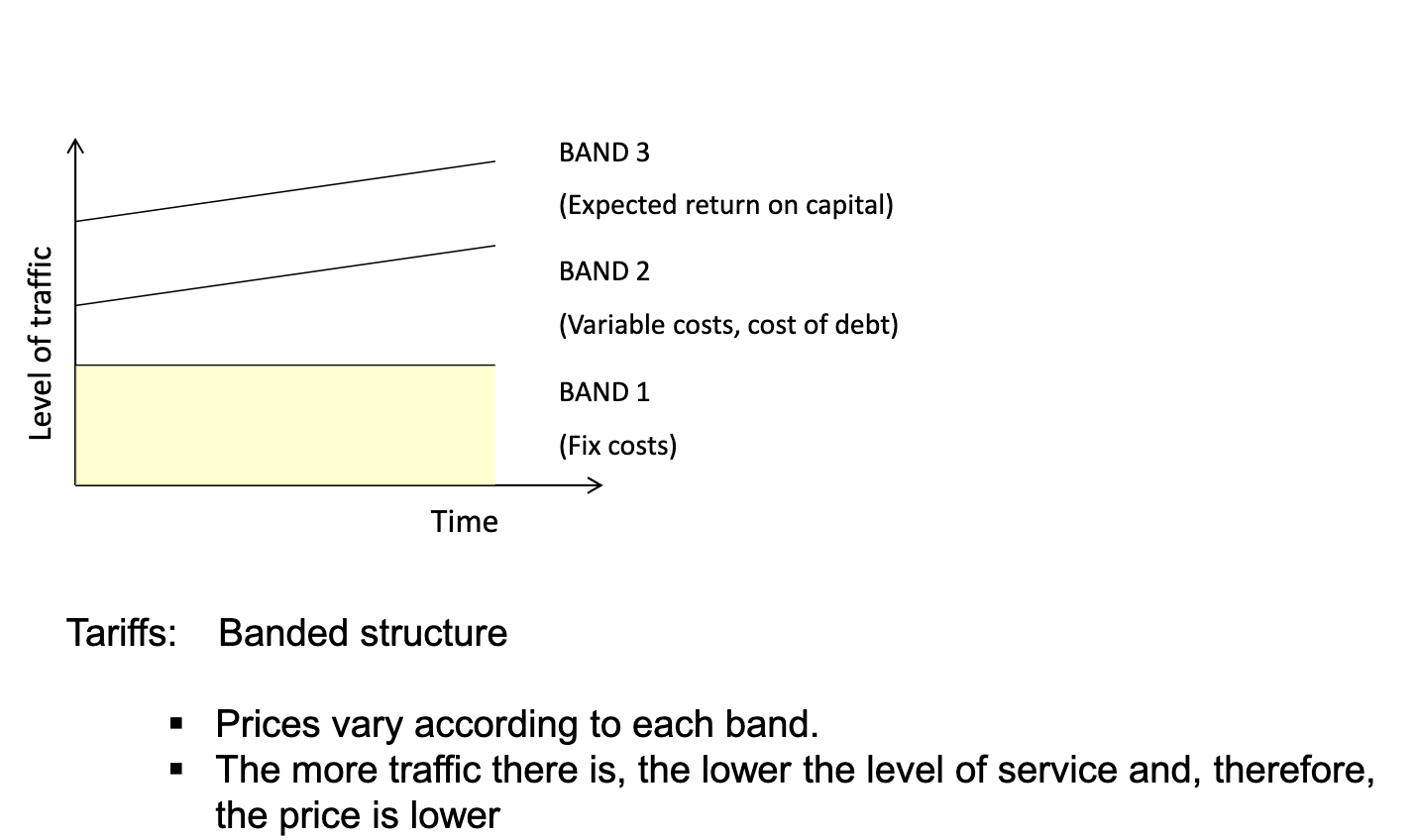
English model - shadow toll
It's a concession system in which the private sector is funded receiving from the public administration a toll or fee proportional to the use of the infrastructure. This happens until the project is completely paid back.
Private financing concessions
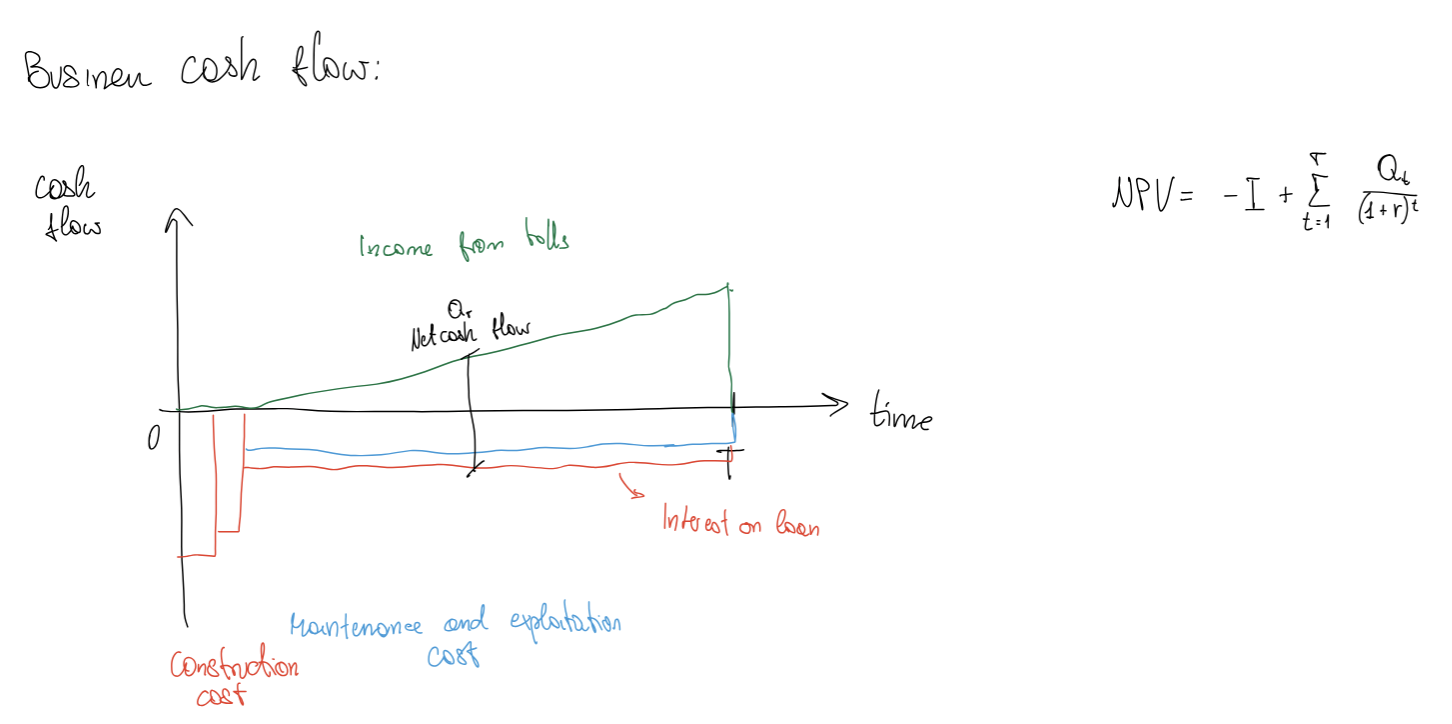
It's a type of contract often used for infrastructures.
- The public gives the private "ownership" of the asset
- The private builds and manages the asset at their own expenses and gets all the profits
- After a defined period, the asset go back to the public
This model allows the public sector to make more public investments.
The contract:
From the company perspective, the goal is:
- Build and maintain
- Manage
Then they get a tariff from the infrastructure that they use to pay: - Exploitation costs
- Payback of the investment
- Capital cost
Risks of concessions
- Construction and expropriation costs
- Operating costs
- Financing costs
- Demand
Risk management - Account for:
- Probability of occurrence
- Potential impact on cash flows
Risk management
RISK TRANSFERRED: Make it so someone else has the burden of the risk. For example, if managing an highway with shadow tolls with bands, if no one uses the infrastructure is the government that has to pay extra.
RISK ASSUMED: The risk needs to be incorporated into the cash flow. The operating company has the burden of the risk.