02 - Procurement and Planning - ISC
02 - Procurement and Planning - ISC
[[2 - Supply planning - SC.pdf]]
Customization and Postponement
Postponement
Postponement is the delay or defer of the final part of production process untile the latest time possible.
Postponement benefits
- Service improved dramatically
- Less complexity
- Flexibility to fit demand
- Inventory levels declined
- Lower storage costs
Postponement needs
- Modular design of products
- Feasible to decouple primary & postponement operations
- High value products
- Flexible production capacity
- Short & reliable lead time
Customization
Customization is a production/preparation process where the output is tailored to the requirements of the customer.
Dell allows you to fully customize your computer upon purchase: processor, memory, storage...
Customization benefits
- Higher added value
- Can charge a premium price
- Method of differentiation
- Builds brand strength & loyalty
- Produce to order, lower inventory
Customization needs
- Lean and Efficient SC process
- Close integration with suppliers
- Effective use of information
- Flexible production capacity
- High degree of automation
Demand planning
Demand planning is the science of planning customer demand to give visibiity to business and SC.
It is important to keep in mind that the forecast will NEVER be correct.

Demand planning KPI
SSP1/SSP3
It's the ratio between the actual units sold and the forecast minus 1. It's calculated at 1 month and 3 months:
- Perfect SSP = 0%
Forecast accuracy
❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗
❗❗❗ COMPLETARE ❗❗❗
❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗
- [?] I don't understand what the symbols mean. How is this calculated?
SELL-IN VS SELL-OUT
Sell in:
- From You to the client: Quantity selling to the client
- What your client is selling to the consumer
What information would you prefer to have if you had to choose: The SELL-OUT
I can predict the sell-in based on the sell-out.
In an ideal world, Sell-IN=Sell-OUT.
Often we don't work with sell-OUT, because the client doesn't disclose it (at least for free).
SELL-IN - What you sell to the costumer
SELL-OUT - What the costumer sells to the final consumer
Demand planning
Bullwhip effect
The bullwhip effect is a demand distortion that travels upstream in the supply chain from the customer to the wholesaler, manufacturer and supplier due to the variance of orders which may be larger than that of sales.
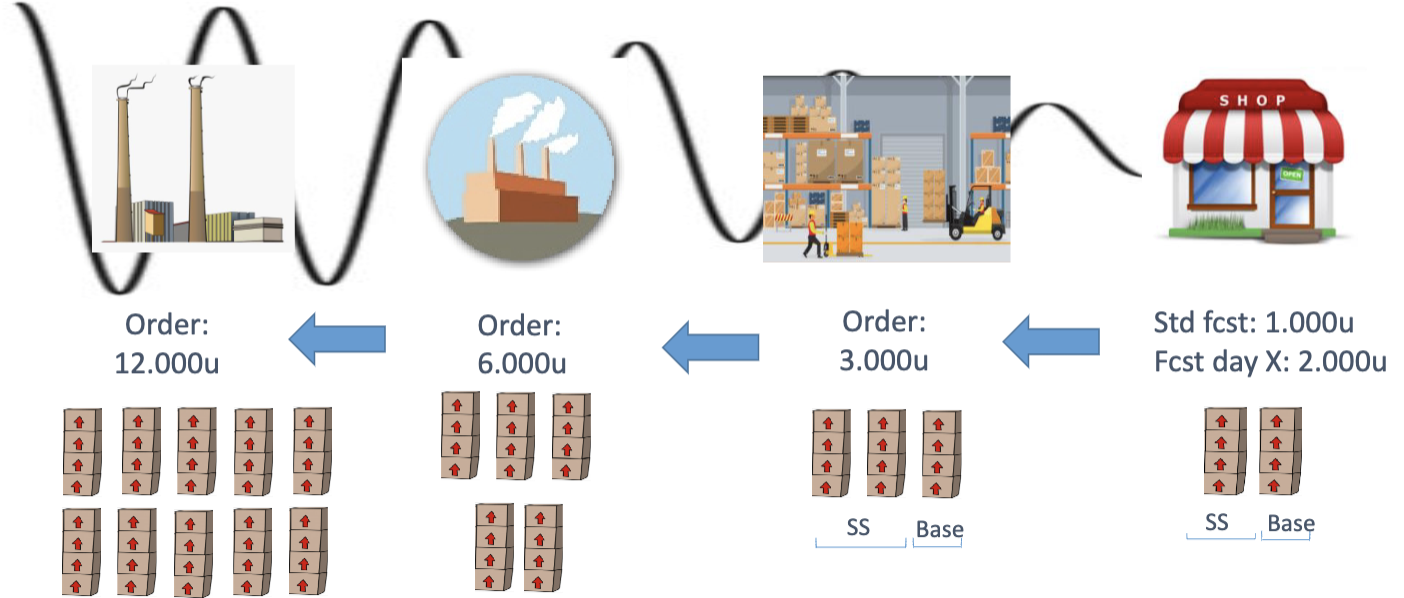
We always sell 1000u + we have 1000u of safety stocks
One day we sell 2000u.
This might induce to send 2000u+1000u to refill (the sold + the new stock).
This can reflect in any step of the supply chain since there are always safety stocks.
Diapers
It seemed they were selling more size 4 diapers than usual.
It seemed they were doing very goood. Then the supermarket stopped asking for refill.
What happened is that the white brand of the supermarket run out, so they sold more pampers. When they restocked, they stopped selling pampers.
EXAMPLE 2
Volvo. They had a lot of green cars. So they started lowering the price of the green cars. So they started to sell more green cars. As a result the factory started producing more green cars.
Bullwhip effect Causes
Main causes of Bullwhip effect:
- Lack of communication/information
- No forecast visibility
Other causes:
- Sales manage
- Operational
- MOQ (Min Order Quantity)
- Sometimes I can't ask for exactly the amount of units I need
- Lot size
- Frequency (Lead times)
- If I can only order once per month, I have to order enough for the whole month
- MOQ (Min Order Quantity)
- Prices
- Discounts can increase demand unexpectedly
Bullwhip effect Solutions
- Decision process
- Understand the problem
- Physical distribution
- Decrease lead times
- Proper SS strategies
- Information
- Try to share the information across the supply chain
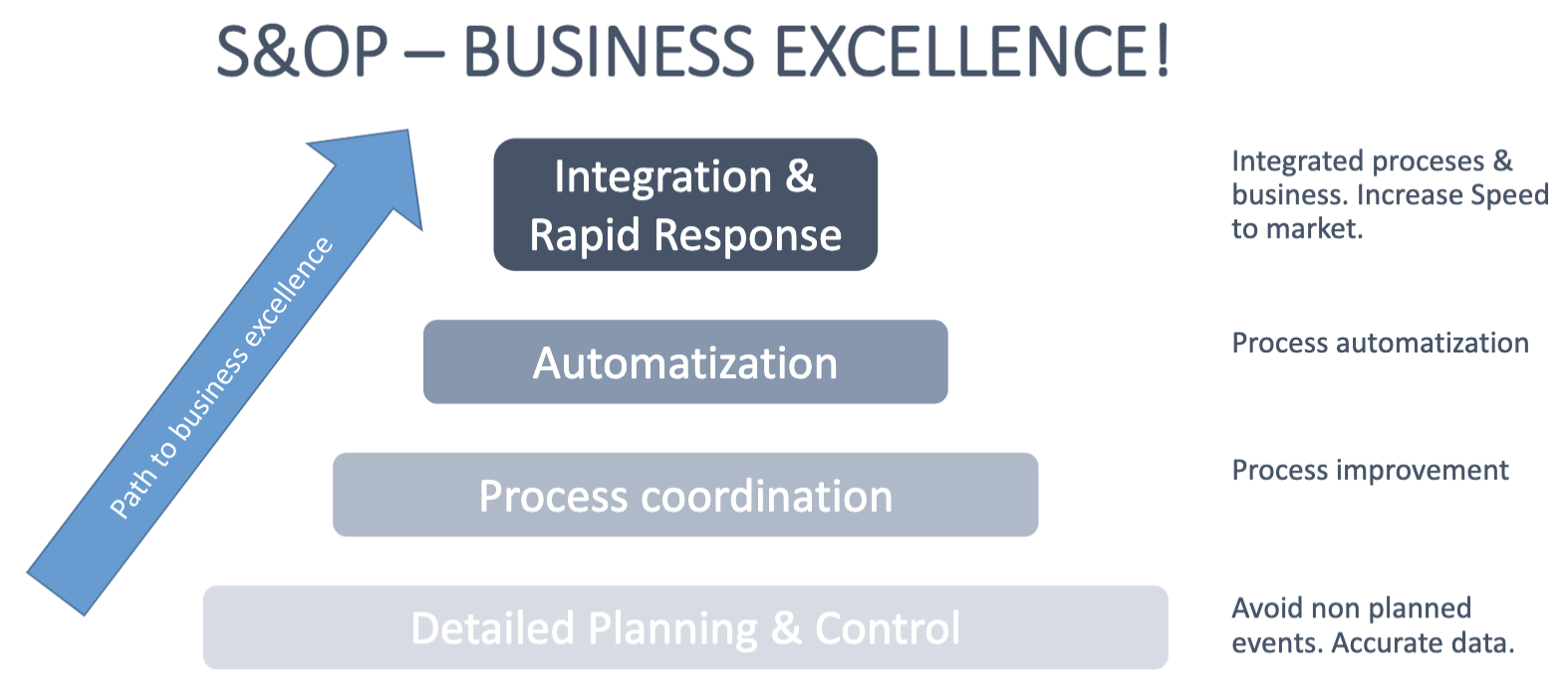
Sales and Operation Planning
The Sales and Operation Planning (S&OP) is a process that efficiently manages launches, demand & supply to meet the needs of customers and consumers
Characteristics:
- Cross functional process - everybody is involved
- Is performed in a monthly basis
- Focus on building long term and sustainable success
- Promote business transparency to take actions to grow
- Disciplined preparation and decision making process with clear actions to the different streams
S&OP Meetings
It's carried out through 4 meetings per month:
- Week 1 - #S&OP - Initiatives
- Week 2 - #S&OP - Consolidation
- Week 3 - #S&OP - Supply
- Week 4 - #S&OP - Category review
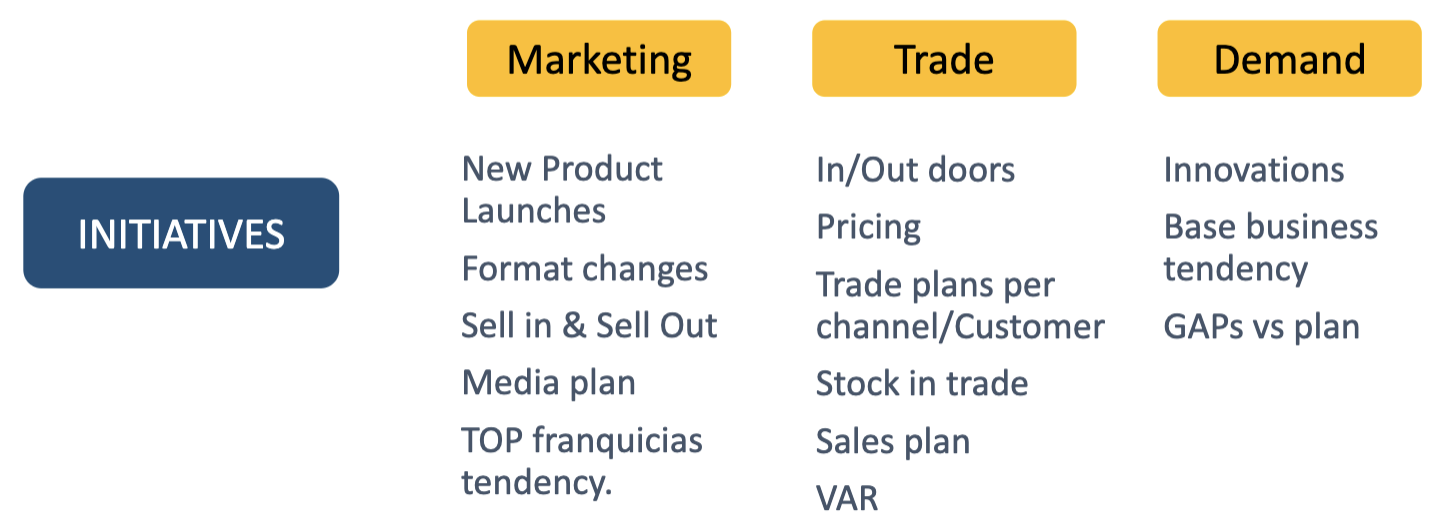
S&OP - Initiatives
-
Doors: ex. how many supermarkets are you selling to
-
TOP Franchises tendency
- Groups of the same product
Every one should be on the same page, but everyone is separated
S&OP - Consolidation
Meeting 2: CONSOLIDATION meetings:
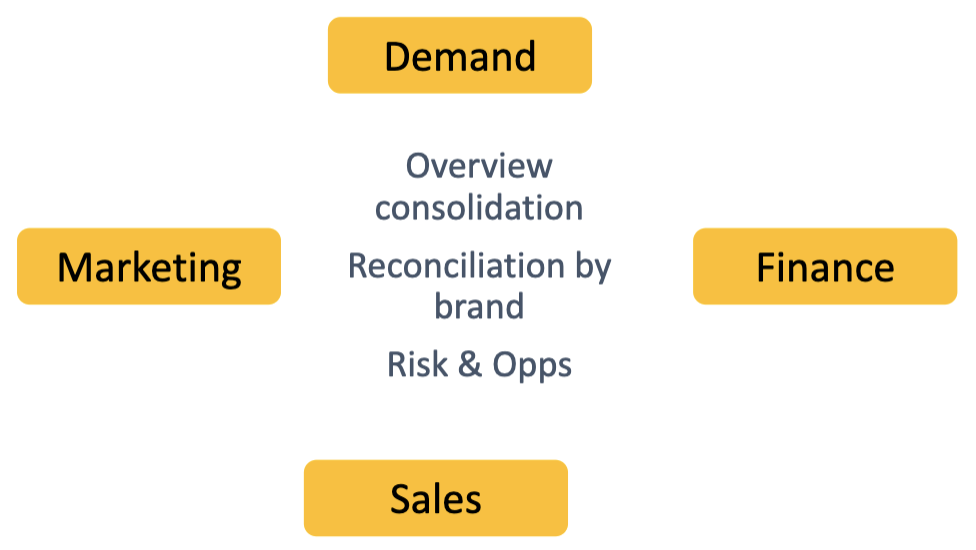
It's the moment to take decisions.
We bring information together and come out with numbers. Then we reach an agreement with the rest of the team
S&OP - Supply
Meeting 3: SUPPLY
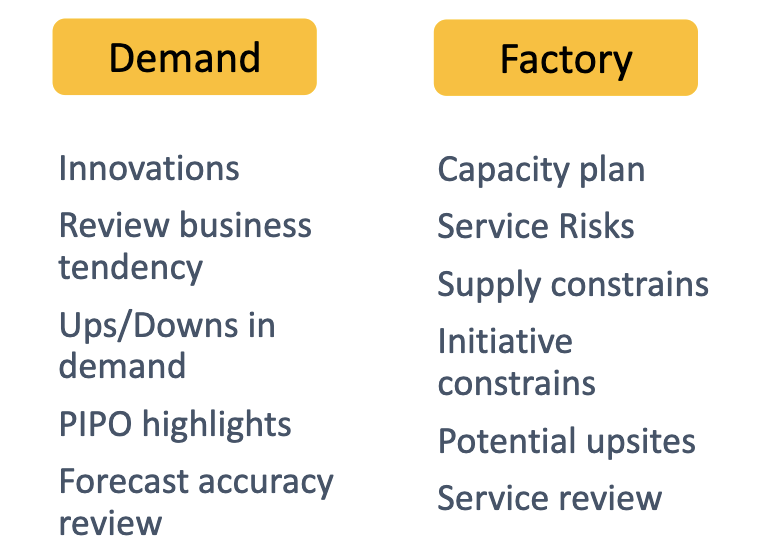
S&OP - Category review
Meeting 4: CATEGORY REVIEW
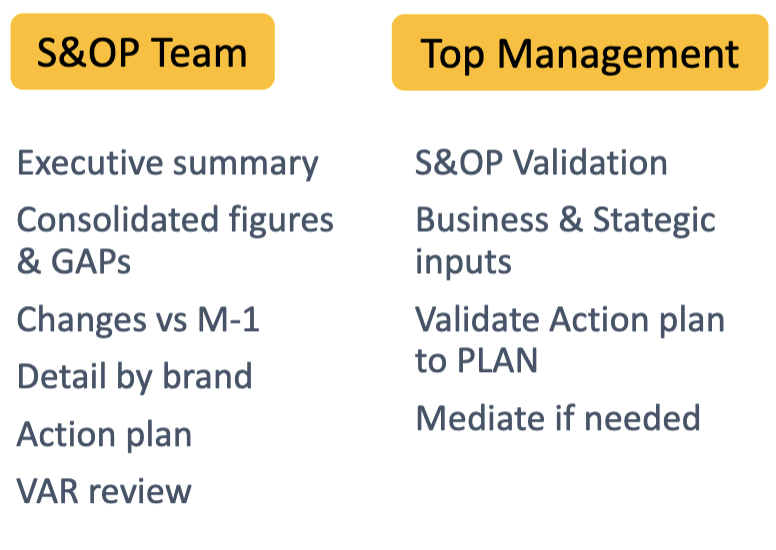
summary:
-
Understand market
-
Bring information together
-
Understand if the factory can deliver
-
Implement
-
What to sell
-
Can we sell it
-
Agree with management to do it