02.1 - Procurement - ISC
02.1 - Procurement - ISC
Function of procurement
- Purchase of products/materials
- Determine best cost/value
- Track and record orders
- Manage supply
- Analyse
The main thing:
BUY AT BEST PRICE
- As procurement you want the best out of the supplier. It's a win-lose (under traditional view)
Modern view of procurement
- Define procurement roadmap
- Global sourcing strategies
- Risk management
- Be a key player in the budgeting process
- Monitor and report Procurement KPI
- SRM (Supplier Relationship Management - SRM)
- Adapt best practices
- External innovation
- Innovation also comes from the different suppliers
- Manage purchasing operations
Supplier - Buyer, in the modern view, becomes a win-win
Also look at the goals of the suppliers. They become partners.
- Supply chain vs procurement vs sourcing vs purchasing
- Supply chain
- Procurement
- Sourcing - management aspect
- Purchasing - operational aspect
- Procurement
- Supply chain
Procurement process
It all starts with the needs
Companies only buy if there is need
9 phases:
- Sourcing
- Needs
- Purchase requisition: converting need in what is needed to buy
- Asses and select vendors
- Purchasing
- Negotiate Price and T&Cs (Terms and conditions)
- Purchase order
- Goods Recept + inspection
- Payment
- 3-way matching
- Approve invoice and peyment
- Keep records
Example:
Need a car? What would you consider when buying a new car or a second hand car:
- Price
- Kilometres
- Social status
- Emissions
- Design
- Ready to go or have to wait to get it
- Technology
- ...
Really need a car?
First you need to assess if you actually need a car.
Buying a car is "Purchase". The "need" is transportation (moving from point A to B).
Supplier assessment and selection
There are 2 main kind of suppliers:
- Direct: They deliver you the things you need for your product (Ex. Bottle <- cap, bottle, targetta)
- Indirect: They deliver what you need to make your company work (Ex: office supplies)
Freight company is kind of hybrid. It depends on the company.If you buy a product that costs 100€ + 5€ transportation, we can consider transportation direct (the product costs 105€), or indirect (the product is direct, 100€, transportation is indirect, 5€).
Supplier evaluation
- Cost (the amount) & cash (how and whenthe payments are done)
- Service
- Capacity
- supply
- Security of business
- Long term relationship
- Making sure the supplier is financially stable
- Innovation
- ESG
- Environmental, Social and Governance
Kraljic matrix
Categorize the suppliers.
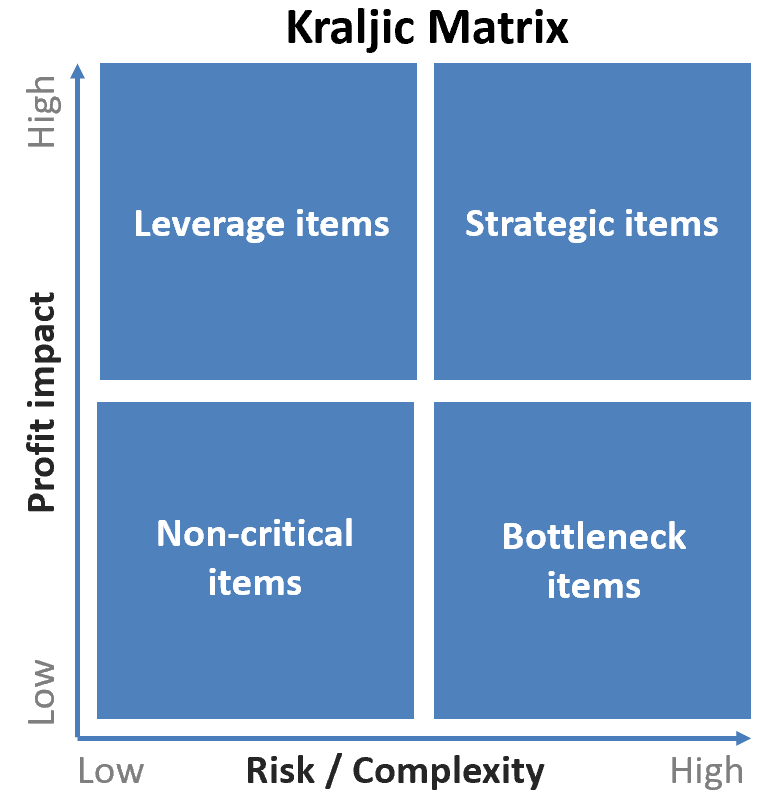
❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗
❗❗❗ COMPLETARE ❗❗❗ Description (bottle necks,...)
❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗
Sourcing strategy
We have a need and as procurement we have to define a strategy.
Each area of a company has its own need. Procurement is in the middle and needs to manage everything.
Porter Forces
Competitive rivalry:
- Buyer Bargain power (ex. Phone carrier: customers can change easily)
- Supplier bargain power (ex. car components: many different suppliers. Power is very low. you can switch easily)
- Threat of substitution
- Threat of new entrance (ex. if you have a coffee shop, it's easy to open a new shop. A space agency it's difficult to replicate)
Strategy definition
- Make or buy
- Decide if we make the product in house or we have another company make the product
Risk assessment
- Identify
- Assess
- Control & priority
- Mitigate
Risk examples:
- Geopolitical crisis
- Currency exchange rate volatility
- Natural disasters
- Bribery
- Capacity
Risk assessment matrix
Risk mitigation
- Double sourcing
- safety stocks
- Long-term contracts
- Capacity expansion
- Not expose to exchange rate
- Anticipate regulatory aspects
- Assess conflict areas
- Shorter supply chains
- Ethical & social aspects
- Frequent audits