01 - Introduction to supply chain - ISC
01 - Introduction to supply chain - ISC
Supply Chain is all the steps necessary to bring a product from the first supplier to the consumer.
It can be defined as the system of suppliers, manufacturers, transportation, distributors, and vendors that exists to transform raw materials to final products and supply those products to customers.
What makes Amazon Prime good for the consumer:
- Easy to use, simple, flexible, fast/quick
- Cheap
- Assortment
- Different per country
- Wide range of products
- Reliable
- Priority
- Sense of security
- Reverse logistics
- Associated products
- Orientated
- No real competitor
- Lots of delivery options
- Distribution of small businesses
The ones in bold, are related to [[Supply Chain]].
Covid-19:
- Everything stopped
- Lack of essential products
The objective of Supply Chain is to have:
- The right product
- at the right place
- at the right moment
- at the right cost
- with the right quality
Supply chain is NOT a synonim of logistics.
Logistic is just a part of supply chain: it's the part when you deliver the product.
Supply chain is the entire process: from raw materials to the shelves.
According to Zara Founder Amancio Ortega:
The Supply Chain is our business model
3 things move across the SC:
- Products
- Cash
- Information
Historical evolution of SC
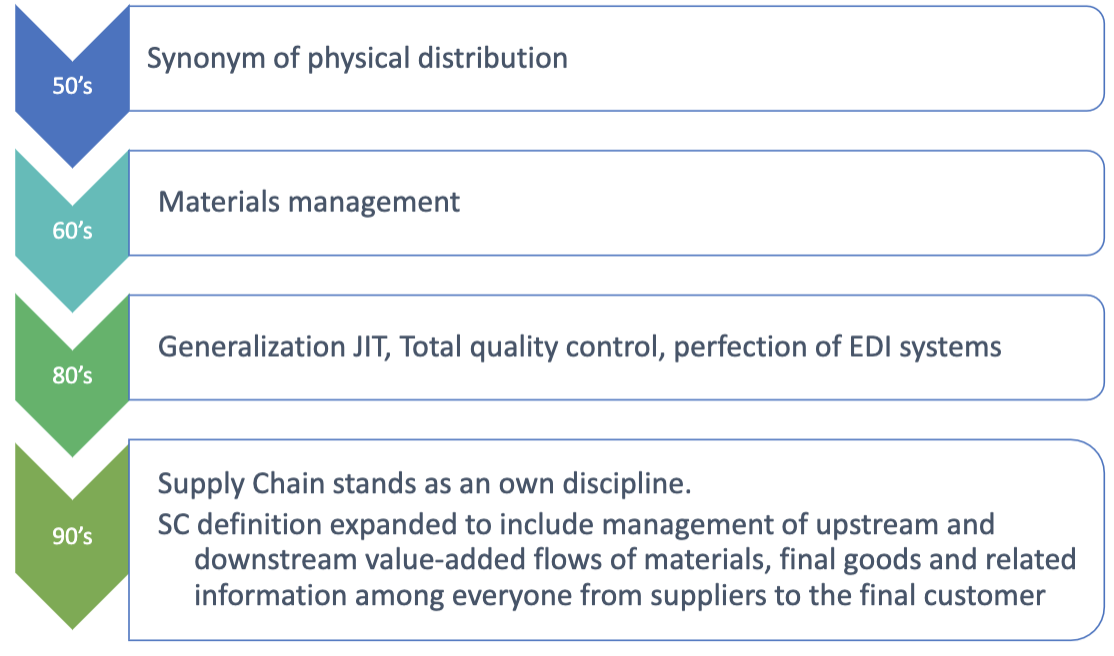
- 50's: Supply Chain is just a synonym of physical distribution
- 60's: It's material management
- 80's: Generalization JIT, Total quality control, perfection of EDI systems
- 90's: Supply Chain stands as its own discipline
Key elements
Departments of Supply Chain:
- #Procurement & materials planning
- #Production & logistics
- #Warehousing, transport & logistics
- #Demand & supply planning
- #Costumer service
Procurement
The procurement department is the one responsible for making sure we get the material.
- They ensure the sourcing of materials.
- Negotiate for good pricing
Roles:
- Identify needs & create process for direct (the product itself) and indirect (what is needed around the product - all the needs that you can't attribute directly to the product) spend.
- Reduce risk and ensure the security of supply
- Ensuring you always have enough material
- Lead E2E (end-to-end) purchase process
- Contracts negotiation & approval
- Lead innovation & quality & saving projects
- Build suppliers collaboration (from "vendors to partners")
Production & logistics
The production and logistic department is responsible for managing and optimizing.
- They produce the service or the product
- They are also responsible for quality control
- They manage workers: safety, conditions,...
- Research and development
- Master plan schedule (what to produce and when to meet the needs of the costumers)
Roles:
- Master plan schedule to fit demand
- Produce dependent & independent demand
Dependent demand
Dependent demand is the demand of all the things needed to produce the final product.
3. Technical packaging
4. Innovation & continuous improvements processes & tools
5. Quality control
6. Ensure right HS&E (Hygiene, Safety and Environment)
7. Cost control
### Warehousing
1. Storage, warehousing & materials handling
2. Define warehouse & logistic network aligned with business needs
3. Define optimal routes and transportation methods
4. Execute internal product movements in-between internal warehouses
5. Order & picking preparation. Deliver OTIF (On Time and In Full - How many times we deliver the complete quantity requested in time) to costumers
6. Inventory management
### Demand & supply planning
1. Forecasting/predicting how many units will be sold, for next 18 months
2. Lead S&OP process. Link between business & global planning
3. Ensure supply: right product in right place at right moment. Lead RCA (Route Cost Analysis - when you don't have the right number of a product, you try to understand why you're not at target and what to do get there)
4. Launches & Promos. Customization readiness
5. PIPO (Phase In - Phase Out) management
6. NPI (New Product Introduction) management
### Costumer service
1. Order entry & management
2. Customer face - SPOC (Single Point of Contact) with costumers
3. Stock control tower & delivery creation
```ad-note
title: Stock Control Tower
Stock control tower:
Let's say we have 3 oprders of a product:
- 1 --> 100
- 2 --> 200
- 3 --> 500
We need 800 units in total.
We convert order in delivering --> confirmation
If we only have a total stock of 500, we can't deliver to everyone. How we choose whom to send and whom not, is managed by Costumer Service.
- Build customer collaboration
- Billing process
- Claims & returns Management
- Master data - people in charge of ensuring that the data managed in the company is correct (price, billing name, unites, etc...)
Push & Pull SC
Depending on weather the production is on demand or the company simply keeps producing the product anyway, the Supply Chain can be categorized as a:
Toilet paper: is a push product
Expensive cars: is a pull product
Push SC
In a Push SC, we never wait for orders in order to produce the product. We have to produce a lot of it.
A push SC has the following characteristics:
- Low production costs
- Low volatility
- Demand driven
- Proactive
- Standard production
- Short lead time
Postponement is a production system based moostly (about 70%) on a #Push SC, that, just for the final part, holds the product and personalizes it according to an order.
It basically convert to a #Pull SC just for the final part.
Pull SC
In a Pull SC, we wait for an order prior to producing a product.
It has the following characteristics:
- High production costs
- High volatility
- Customer Order
- Reactive
- Customized (receive order with specific characteristics to produce)
- Long lead times
Postponement is a production system based moostly (about 70%) on a #Push SC, that, just for the final part, holds the product and personalizes it according to an order.
It basically convert to a #Pull SC just for the final part.
Examples:
- PUSH:
- Cheap clothes
- Sugar
- Laptops
- Construction materials (usual ones, unless there are some very specific specifications)
- Restaurants
- PULL:
- Public transportation vehicles
Glasses are push for most of it but then it's postponened for the crystal.
Cost vs Value
SC focused on Cost
- Efficiency
- Standardized products
- Keep stock low
| Cost | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Supply product/service at low cost | Quick response to demand |
| Product design | Maximize performance at min cost | Modularity to allow product differentiation |
| Prices | Low margins due to price is the driver of main customers | High margins as price is NOT a driver of main costumers |
| Production | Decrease spend due to high utilization | Keep flexibility with capacity to response to demand variations/changes |
| Stocks | Minimum stock to have low cost | Have stock to response demand variation / supply uncertainty |
| Suppliers | Selection of suppliers based on cost (& quality) | Selection of suppliers based on flexibility, responsiveness & quality |
SC Excellence matrix
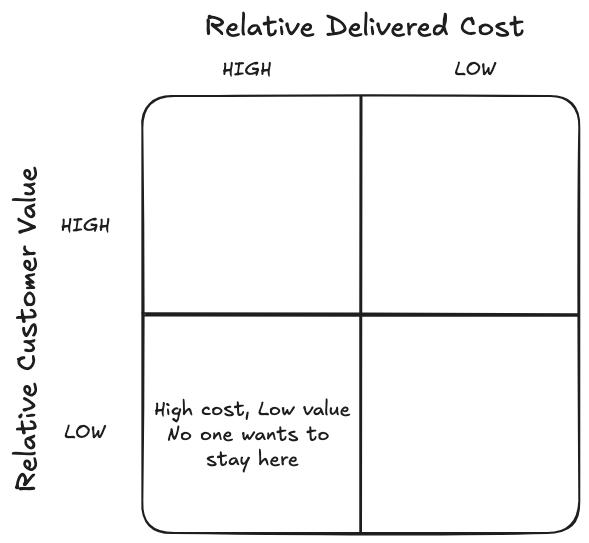
Optimizing the supply chain
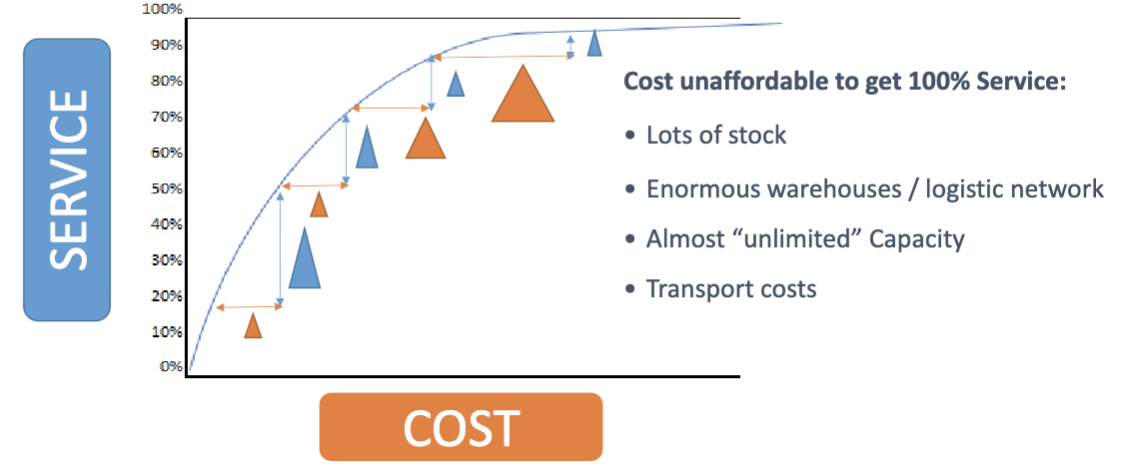
With the increase in service, a higher and higher cost is needed.
The more you grow, the cost grows a lot more than proportionally. There is not a way to have 100% service (always deliver). Usually you stay around 95-96%.
- IKEA: cost oriented. All simple, cheap, min decent quality
- El Corte Ingles (high end): Good costumer care, they are close to costumers, they do almost everything you ask them
- Good negotiations power on a standardized product
- They work with [[02 - Procurement and Planning - ISC#Postponement]]
- strong logistics
QAQC: Quality Control and Quality Assurance.
Tools
Manage, Optimize, Improve
ERP - Enterprise Resources Planning. The software that manages day to day activities across all functions in a company. (Oracle, SAP)
Systems: MPS & MRP
Enterprise Resource Planning is the software that manages day to day activities across all functions in a company. It centralizes all company information making it more standard and accessible.
MPS: Master Production Schedule Plans: when to produce Finish or Semifinished products
MRP: Material Requirements Planning
MRP II: Material + Resources
Distribution Requirements Planning (DRP)
DRP: Distribution Requirements Planning is a adistribution planning and stock mamagement tool, computer based, that answer the questions: how many, when and where it must be replenished.
Planning and CRP
- Planning tools are softwares that provide businesses with forecasting solutions to predict customer needs. These tools analyse historical data to find statistical models to predict the future (SAP, jda)
- CS tools: Customer Service tools manage the order entry/processing & delivery creation
CRP: Costumer Replacement Planning. Part of CS tools.
❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗
❗❗❗ COMPLETARE ❗❗❗
❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗
KPI: Key Performance Indicators