01 - Midterm Exam - DME
01 - Midterm Exam - DME
PDF: ![[1 - MidTerm - DME 1.pdf]]
Soluzione:
Problem 1
Describe briefly:
1.a) In terms of microeconomics, does a long-term cost function have fix costs?
No, a long term cost function does not have fix costs. In the long term, by definition, fix costs become variable. We could look at it like the company changing its size, so, the fix costs, have to vary.
1.b) Indicate the diminishing returns law.
Diminishing return law is the concept for which, despite keeping to increase the production factors (capital and labor) by a significant amount, the production increases less and less.
1.c) In the case of increasing return to scale, Is the marginal cost higher than the average cost? Provide a brief explanation.
No is not. With increasing return of scale, production grows faster than the production factors. This allows for greater efficiency in producing more. In this condition, the average cost decreases with production. Also, because of what has been just said, the cost of producing one extra unit of product must be lower than the unit cost of producing the current amount of units. By definition, the cost of producing one extra unit of product is the marginal cost. The marginal cost must then be lower than the average cost.
1.d) Represent the short-term average cost curve and marginal cost curve.
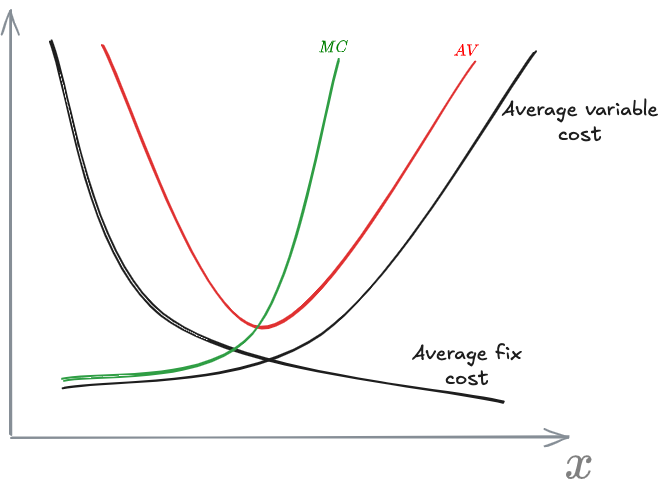
Problem 2
Let’s suppose an economy with only two types of goods,
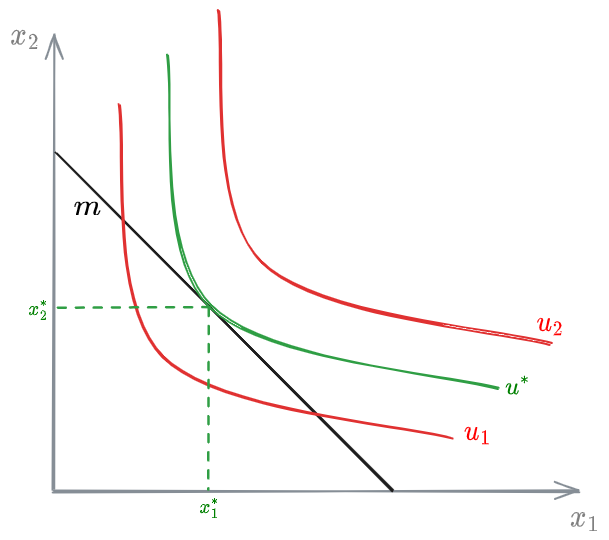
In the graph, the black straight line represent the budget. The curved lines represent 3 possible utility functions such that:
The optimal condition is given by utility function
Problem 3 - Road pricing
3.a) Let’s suppose a road without congestion. “g” is the generalized cost per user, “q” is the traffic flow, “AC” the average cost and “c” the marginal cost. Indicate in the graph the optimal price of the road to maximize the social welfare, the consumer surplus and the producer surplus.
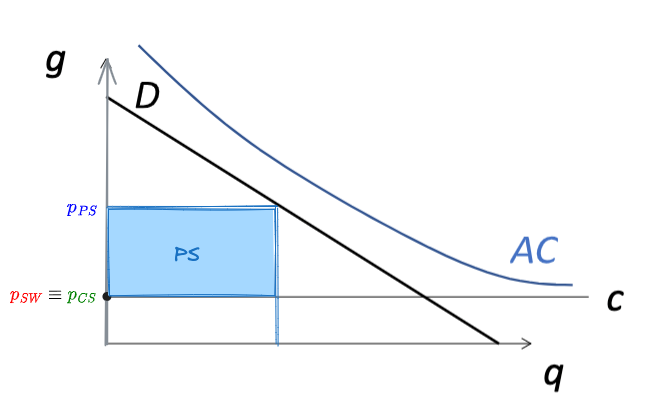
Let’s assume now a road with congestion problems. Represent graphically 1) the average cost, marginal cost, social marginal cost and the optimum level of traffic flow and user’s cost to maximize the social welfare and 2) the toll (or tax) to charge to road user’s in order to reach this optimal point
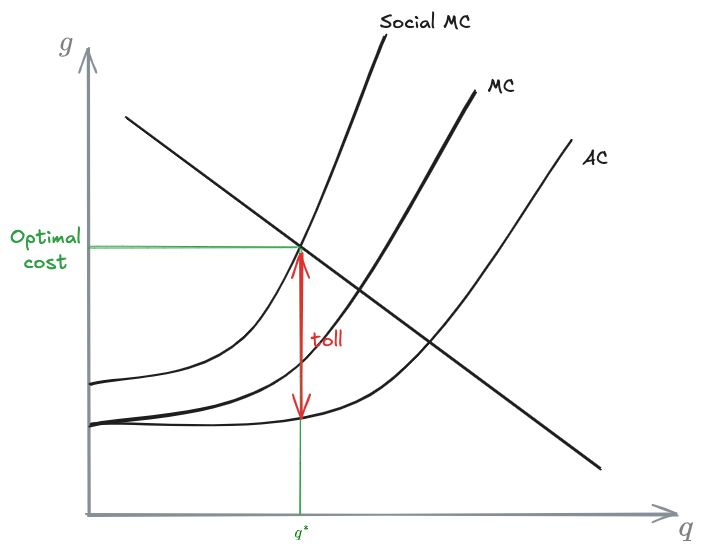
Problem 4
4.a) What should be the main objectives of parking regulation?
The main objectives of parking regulation should be:
- Optimizing parking it self
- Reducing local conjestion
4.b) Justify the economic reason that the public transportation is usually in deficit.
Public transportation is generally thought to maximizing Social Welfare rather than profits. This justifies subsidies. Also, PT often produces positive externalities. These are not gained by the operating company but by the government which is again justified to subsidize the system.